When do you use the different lights on your car?
Proper lighting ensures that you can see the road well (even when it is dark or in bad weather) and that you are visible to others. Before you drive off, check that your lights are working. Check regularly that
- All lights and reflectors are clean
- All lights are on
- Headlights are properly adjusted (have them checked at the garage)
- There are spare bulbs and extra fuses in the car
Driving test checks
During your practical exam, the examiner may ask you to perform a number of control actions.
For example, you must be able to operate the brake lights, turn signals and lights while the examiner checks them from the outside.
Compulsory lighting ‼️
Driving with lights is mandatory:
- At night (*)
- With poor visibility during the day
Drivers of motor vehicles, mopeds, motorized bicycles, mopeds, microcars and motorized vehicles for the disabled must drive with dipped headlights.
Cyclists and drivers of cars (such as cargo bikes) must drive with white front and red rear lights. (**)
* Night means the period between sunset and sunrise.
** Lights on the body: Instead of lights on the bicycle, a cyclist may wear a white light on the chest and red light on the back. However, these lights on the body must be clearly visible to other traffic and must not flash.
Lighting not mandatory, but safer
Lighting during the day is usually not compulsory. Nevertheless, driving with lights is safer when, for example: driving in a tunnel, when the sun is low, during twilight or in situations with poor visibility. Many drivers therefore also drive with lights during the day. 👀
Operation of the lights
The image below shows where to find the controls for the different lights on your car (the exact layout may vary slightly from one type of car to another).
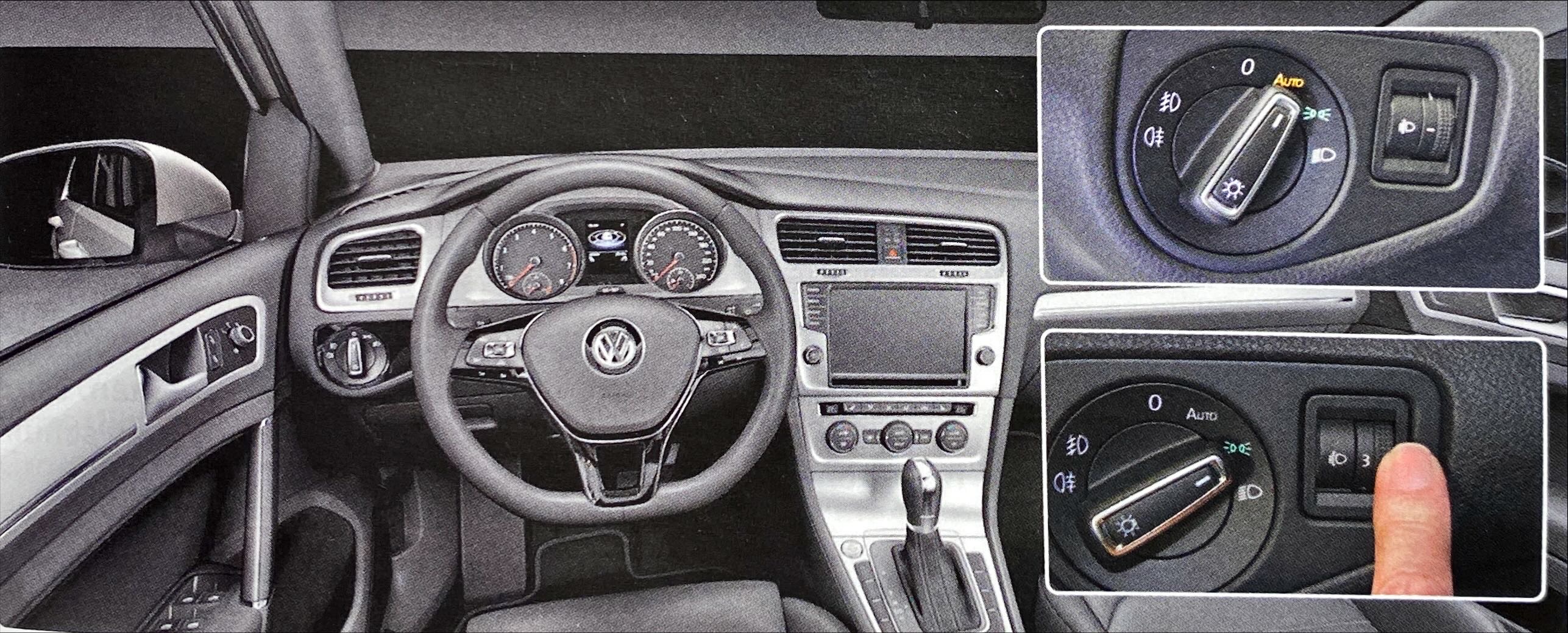

- Low beam (*)
- City light (*)
- Daytime running light
- Brake light
- Reversing light
- High beam (*)
- Fog light (*)
- Direction indicators
- Warning indicators
* With these lights, the rear light is also automatically illuminated.
Lighting front and rear
Front
- Low beam
- City light
- Daytime running light
- High beam
- Direction blinker
- Hazard warning light
Rear
- Taillight
- Brake light
- Reverse light
- Rear fog light
- Direction blinker
- Hazard warning signal
Dim (dipped) lights

If lighting is mandatory, then turn on your dipped headlights. These white or yellow non-glare lights must be angled downward.
City (town) light

City lights consist of two small lights in front, rear lights and license plate lights. These lights make your car visible to others, but do not illuminate the road in front of you. Therefore, driving with only city lights is not enough.
City lights are primarily “parking lights”. If you park your car on the roadway outside built-up areas at night or in bad weather during the day, you must turn on your parking lights.
‼️ Town lights outside built-up areas are mandatory for:
- motor vehicles on more than 2 wheels
- microcars
- trailers wider than 1.60 meters
Standing still outside built-up areas ‼️
Are you standing still outside the built-up area on the carriageway or on a parking or emergency lane, parking or refuge along the motorway or highway? Then city light (with tail light) is mandatory.
Stopping within the built-up area ‼️
Within built-up areas, lighting while stationary is not mandatory. However, it can sometimes be wiser to use sidelights for your visibility in built-up areas.
Stationary trailers smaller than 1.60 meters must only have a rear light on. Stationary motorcycles need not be illuminated.
Daytime running lights
Since February 2011, passenger cars and light vans must have daytime running lights. Daytime running lights are between low beam and city lights and make the car more visible during the day. When starting the engine, the daytime running lights come on automatically. Thus, driving with daytime running lights, is slowly becoming the norm.
High beam

High beam is used when driving on a road (inside or outside the built-up area) in the dark and you cannot see it clearly. The white/yellow high beams radiate far. This allows you to see more of the road ahead.
High beams can blind other road users. Therefore, you should turn on this light only when you are not hindering anyone. ⚠️
‼️ The high beam may NOT be turned on:
- During the day
- With oncoming traffic
- When driving close behind another vehicle
Taillight
These two red lights automatically illuminate simultaneously with city light, low beam, high beam or fog light.
Brake light
The three red brake lights on the back of the car, light up as soon as you brake.
Brake lights can also be used to warn those behind you that you are about to brake. To do this, depress your brake pedal lightly so that the brake lights light up briefly. Your tailgaters now know you intend to brake. Especially on roads outside built-up areas where speeds are higher and little traffic is turning, a signal to your rear driver can’t hurt.
Reversing light
This white or yellow light illuminates automatically when the reverse gear is engaged and while reversing.
Front and rear fog lights
Front:

Rear:

Heavy rain, snow or fog can significantly impair visibility on the road. In that case, you may (in combination with low beam headlights) turn on your front fog lights. Fog usually hangs about 60 cm above the road surface. Fog lights shine low, under the fog. This gives you more visibility when you turn on your fog lights.
In dense fog, high beams are usually unusable. 🤷♂️ The fog bounces the light back, which can blind you yourself. When the front fog lights are on, city lights may be used instead of low beam.
Is visibility less than 50 meters?
Then you may also turn on your rear fog light in fog or snow.
⚠️ In heavy rain, you may not drive with rear fog lights on. This bright red light can blind drivers behind you.
Turn signals
Also: indicators
An important way to let the traffic around you know where you want to go is to use your turn signals.
In these situations, direction indicators are mandatory:
- Pulling away (ie. drive away from parking or standing still)
- Overtaking
- Merging or leaving the highway/freeway
- Changing lanes
- Turning left or right
- Turning at a traffic circle (roundabout)
- Get in lane / sorting (ie. get ready for a special maneuver)
Warning indicators (hazard lights) 🚨

Hazard warning flashers are used, as the name implies, to warn other drivers.
This can be for a variety of reasons:
- You’re encountering a traffic jam and want to warn following traffic
- You are towing a vehicle or being towed yourself
- You have to slow down, stop or stop because of a breakdown, a heavy load or for some other reason
- You are stopped in a place where you should not be
Emergency stop signal
Since January 2010, passenger cars (and commercial vehicles and buses) are allowed to have an ESS system (Emergency Stop Signal system). This system makes the brake lights flash as soon as the car brakes sharply or makes an emergency stop.
Other lights
The lights below are turned on only in conjunction with dipped beam (or front fog light).
Cornering light
Turns with the curve to make it easier to scan the area while turning.
Corner light (side marker light)
Lit at the front corner, illuminates the angle to which the car wants to turn. This is meant to help other drivers to distinguish the car boundaries.
Maneuvering light
White light on the side, to be used during maneuvers with a maximum speed of 10 km per hour.
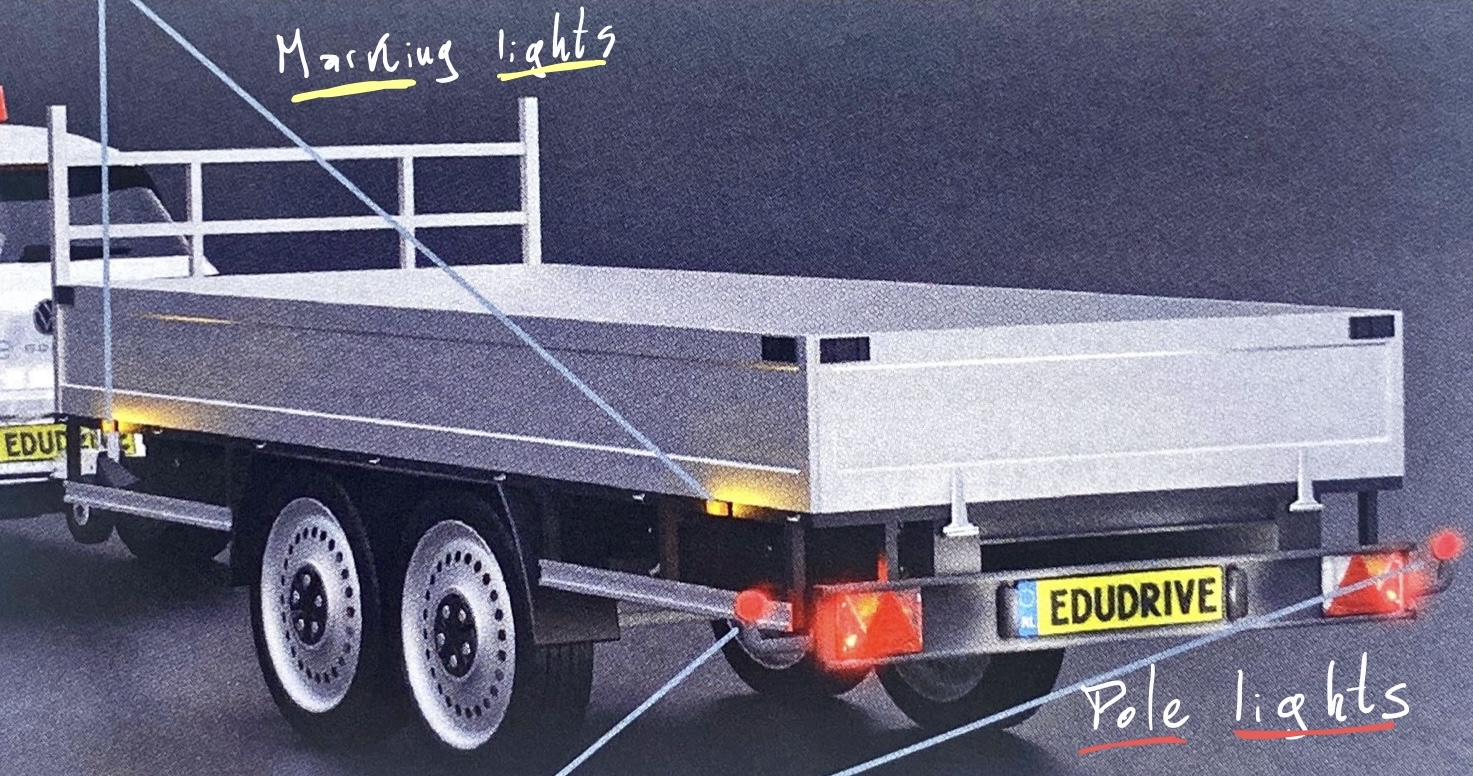
Marking light
Marks the width of a vehicle and/or load. Is mandatory for vehicles wider than 2.10 meters.
Pole light
‘Extended’ tail light, often found on trailers or trucks.
Trailers or trucks often drive with stake/pole lights (an extended taillight).