Foundations of the digital (discrete) revolution
Created: 2022-10-14 10:46
- Digital computers, as opposed to analog ones, have the advantage of being able to do discrete signaling to achieve deep and accurate computations.
- Integrated circuits helped the digital revolution by a lot.
- Society went from material goods based to information services based.
For those 3 reasons arises the information revolution.
And there are some other factors in play as well:
- Computers allow robots to do the hard labor and manufacturing. Products produced by machines have to be adapted to that form of production, which differs greatly from the hand made goods.
- The effect of computer and science is huge. It enables us to do rather impossible tasks had we not had computers. Simulations are way cheaper than actual experiments in a lab. Another product that changed.
- Along the same lines, computers enable engineering. Which take engineering closer to science and the question becomes not so much “what we can do” but rather “what we want to do”.
- Computers enable micromanagement => Micromanagement prevents career growth
- Computers take over the entertainment. If this was true in 1996, how much true it is today Information obesity blended with entertainment. Information as entertainment?
- Information is key in decision making, which is seen so evidently at war. Any field that requires constant decision making will, and is already, changed by computers. All this constant change means one cannot stick to theories of the past, which are taught today (that was true when the book was written and is still true today).
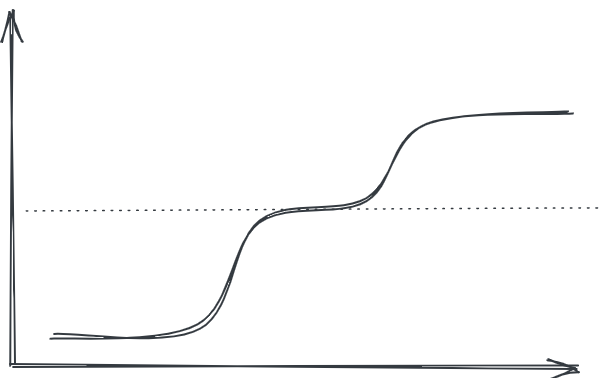
The rate of evolution of a field, which goes from no change to a exponential growth to then stagnant again due to reaching some natural limit.

If we find a solution or a work around to those natural limits we might see another cycle: